我院讲师白琰冰就巨灾损毁评估问题在《Remote Sensing》发表论文
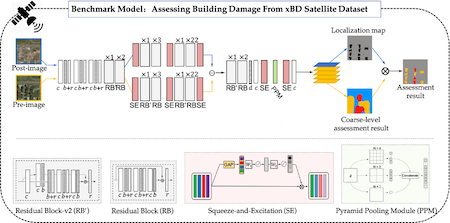
时间:2021-04-07我院讲师、中心研究员白琰冰在《Remote Sensing》发表论文。该研究主要使用来自全世界范围的85万个受灾(地震/海啸、台风、洪水、火山和山火)建筑物损毁相关的大规模卫星影像数据集,构建了基于监督学习语义分割算法的建筑物损毁分类基准模型。该研究引入空洞卷积,设计了一种基于金字塔池化模块的Semi-Siamese 网络,该网络可以同时开展建筑物提取和建筑物损毁分类多任务学习,实现了端对端自动建筑物损毁提取。此外,我们基于该基准模型,开展了针对2011年东日本大地震的建筑物损毁评估模型泛化实证研究。
论文题目
Boosting Poisson regression models with telematics car driving dataPyramid Pooling Module-Based Semi-Siamese Network: A Benchmark Model for Assessing Building Damage from xBD Satellite Imagery Datasets
作者介绍
白琰冰,日本东北大学(Tohoku University)博士,美国加利福尼亚大学欧文分校计算机工程学院访问学者。现任职中国人民大学统计学院数据科学与大数据统计系讲师,硕士研究生导师,应用统计科学研究中心研究员。中国人民大学杰出青年学者,北京大数据协会理事会理事,曾获美国微软公司人工智能科研奖励。研究兴趣为计算机视觉,时空大数据分析,分布式计算等。承担中国人民大学研究生大数据分布式计算和本科生并行计算与软件设计等课程的授课工作。

英文摘要
Most mainstream research on assessing building damage using satellite imagery is based on scattered datasets and lacks unified standards and methods to quantify and compare the performance of different models. To mitigate these problems, the present study develops a novel end-to-end benchmark model, termed the pyramid pooling module semi-Siamese network (PPM-SSNet), based on a large-scale xBD satellite imagery dataset. The high precision of the proposed model is achieved by adding residual blocks with dilated convolution and squeeze-and-excitation blocks into the network. Simultaneously, the highly automated process of satellite imagery input and damage classification result output is reached by employing concurrent learned attention mechanisms through a semi-Siamese network for end-to-end input and output purposes. Our proposed method achieves F1 scores of 0.90, 0.41, 0.65, and 0.70 for the undamaged, minor-damaged, major-damaged, and destroyed building classes, respectively. From the perspective of end-to-end methods, the ablation experiments and comparative analysis confirm the effectiveness and originality of the PPM-SSNet method. Finally, the consistent prediction results of our model for data from the 2011 Tohoku Earthquake verify the high performance of our model in terms of the domain shift problem, which implies that it is effective for evaluating future disasters.
发表页面